Economic impact
Humans depend on the natural world for food, fuel and other resources. If they are depleted or altered then there is a cost.
Some species are pests of agricultural or other products, which can dramatically reduce yields and the income they generate.
By studying these species, Museum scientists can learn more about their distribution and behaviour, and suggest ways of helping to control them. Find out more about the species below.
-

Agathiphaga vitiensis (Fiji kauri moth) - 17/09/2010
Agathiphaga vitiensis is an unusual moth found in the south western Pacific. Its larvae live on Kauri pine trees, where they develop in seeds within the pine cone. It is rarely seen in the wild, but in the 1970s, Museum scientists raised adults from infested pine seeds. This primitive moth is now helping scientists understand the evolutionary relationships between moth species and their close relatives, the caddis flies.
-

Aleurodicus dispersus (spiralling whitefly) - 05/01/2010
The spiralling whitefly, Aleurodicus dispersus, is a widespread pest that is costing millions of dollars in lost yield in agricultural crops across the tropics. Its widespread distribution is an example of failed quarantine procedures. Find out more about the spiralling whitefly and what is being done to manage its impact.
-

Atta (leafcutter ants) - 21/10/2010
Leafcutter ants are the subject of the Veolia Environnement Wildlife Photographer of the Year 2010 winning photograph. Ants in the genus Atta harvest leaves to cultivate fungus that they then eat. Castes of ants fulfil a range of tasks including collecting vegetation, tending fungus gardens, construction and defence. Find out more about this fascinating species.
-

Azolla filiculoides (water fern) - 15/11/2010
Azolla filiculoides is a tiny invasive fern that has spread around the world, but can be put to good use. It thrives in nutrient-rich ponds and ditches, where it forms potentially damaging thick mats of foliage. Azolla can be a useful fertiliser, thanks to a nitrogen-fixing alga that lives in it, and so is often used in paddy fields to improve rice yields. Take a closer look at this floating fern.
-
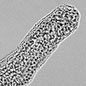
Buddenbrockia plumatellae - 09/07/2010
Buddenbrockia plumatellae is a tiny worm that is parasitic in freshwater bryozoans and so unknown since it was first described in 1910 that giving it a place in the animal kingdom has only recently been achieved. Find out more about this species.
-

Catagonus wagneri - 29/11/2010
The Chacoan peccary, Catagonus wagneri,was discovered in the remote Chaco forest in Paraguay, in 1975. Before its surprise discovery, scientists assumed it was extinct as it was only known from fossilised remains. Find out what threatens the Chacoan peccary today and what more can be done to protect this living fossil.
-

Ceiba chodatii (palo borracho, palo botella, samu’u) - 27/11/2010
Ceiba chodatii is a deciduous tree commonly found in the Dry Chaco of Paraguay. Its characteristic bottle-shaped trunk makes it easy to spot and helps it survive in its arid habitat. Local people use the tree in a variety of ways, from crafting canoes to curing headaches. Read on to discover more about palo borracho (the drunken tree) and its many uses.
-

Conopeum seurati - 13/03/2010
Conopeum seurati is found in estuarine habitats from Northern Europe to as far as New Zealand. Find out more about this bryozoan.
-

Dendrolimus pini (pine-tree lappet moth) - 11/01/2010
Find out more about the widespread Dendrolimus pini, including how it came to be discovered in Britain and the impact it is having on forestry trees.
-
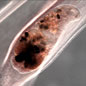
Derogenes varicus - 14/08/2010
Derogenes varicus is a tiny flatworm that lives in fish that inhabit cold waters around the world. The flatworm has a complex lifecycle that involves three hosts, a marine snail, another invertebrate and a fish. The worms tail is central to its success which it uses for protection, propulsion and as a way of infecting one of its hosts. Read on to find out more about this intriguing parasite.
-

Fredericella sultana - 14/04/2010
Fredericella sultana is freshwater bryozoan commonly found in flowing or turbulent waters such as rivers and streams. It forms colonies of identical zooids, can resemble plants and is preyed on by waterfowl and fish. Find out more about one of the most common freshwater bryozoans in the world, Fredericella sultana.
-

Hedera helix (ivy) - 08/12/2010
Ivy is one of the few woody vines growing in Britain, and is commonly found as a ‘living curtain’ clinging to buildings and trees. It flowers and produces fruit late in the year and is often used as part of Christmas decorations. There are many ivy varieties, but it is still unclear how many species exist. Find out more about this climbing evergreen plant.
-

Melolontha melolontha (cockchafer or May bug) - 20/05/2010
Melolontha melolontha is the largest species of chafer beetle in the UK. It is seen flying between the months of May and July and often enters homes through open windows or chimneys, attracted by the artificial light. Find out more about this species.
-

Paralecanium expansum metallicum (scale insect) - 10/02/2010
Paralecanium expansum metallicum is a scale insect with a remarkable appearance, like a splash of metal solder on the surface of the leaves it feeds on. Find out more about this species.
-
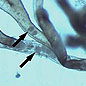
Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae - 22/03/2010
Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae is a multicellular endoparasite known for causing proliferative kidney disease in trout and salmon, which has resulted in significant economic losses for aquaculture and has threatened wild fish populations. Find out more about Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae.
-

Ananas comosus (pineapple) - 02/11/2010
The pineapple, Ananas comosus, was first discovered by the Tupi-Guaraní Indian tribe in what is now Paraguay. Ananas comes from the Tupi word meaning excellent fruit, and the name pineapple was coined by European explorers who noticed the fruit’s similarity to pine cones. Find out more about this succulent fruit and its many uses.
-

Ilex paraguariensis (yerba mate) - 01/12/2010
Ilex paraguariensis is a member of the holly family and is an evergreen tree that grows up to 18 metres tall. For generations, it has been used in Paraguay and other parts of South America to make a herbal infusion known as yerba mate, or Paraguayan tea. Discover the plant’s many beneficial properties and how yerba mate has become one of South America’s biggest exports.
-

Leptoglossus occidentalis (western conifer-seed bug) - 26/11/2010
Leptoglossus occidentalis is an invasive insect that has spread from North America to Europe in the last 10 years. It is an agricultural pest that feeds on pine trees and can cause significant seed loss in commercial tree crops such as the Douglas fir. Find out more about this 'leaf-footed' bug.
-

Macrocystis pyrifera (giant kelp) - 06/10/2010
Macrocystis pyrifera, is a giant among seaweeds. Its fronds can grow up to 45m long in a single season and it forms extensive underwater forests that create the base for an ecosystem of hundreds of marine animals. For years it has been harvested for commercial purposes. Find out how this seaweed is exploited, and what threatens its survival.
-

Sminthurus viridis (lucerne flea) - 28/09/2010
Sminthurus viridis is a springtail species that is native to Europe but, since its introduction to the southern hemisphere, has become an agricultural pest. This tiny animal can decimate crops such as clover and lucerne as numbers reach a million per square metre. Discover more about the life of the lucerne flea, and how recent DNA studies are helping scientists explore the springtail's evolutionary relationship with insects.
-

Tetrao urogallus (capercaillie) - 30/11/2010
The capercaillie is a most charismatic grouse, found in Scotland’s pinewood forests. It feeds on plants, seeds and even pine needles. The birds use open spaces within the woodland to perform an unusual mating ritual called ‘lekking’. Discover more about the habits of this majestic bird and find out what conservation efforts are underway to bolster its dwindling numbers.
-

Welwitschia mirabilis (tree tumbo) - 13/11/2010
Welwitschia mirabilis is a remarkable plant that can live for over a thousand years in an inhospitable desert habitat. It has a short stem and 2 huge leaves that take in water from fog and dew. The plant is a relic from the Jurassic Period and has changed little over millions of years. Discover more about the life of this ‘living fossil’.
