Pediculus humanus (head or body louse)
The louse Pediculus humanus is an ectoparasite of the human head or body.
The head louse variant is common in the western world, the louse feeding on blood of its human host. Infection rates exceeding 20% reported from selected primary schools in Australia, the UK and USA.
The body louse variant can carry typhus and was responsible for hundreds of millions of deaths up until the early nineteen hundreds.
Species detail
-
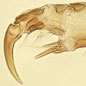
Taxonomy
Discover more about the physical characteristics of Pediculus humanus.
-
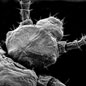
Distribution
Pediculus humanus are found worldwide, living as an ectoparasite on humans, learn more about the other species thy can inhabit.
-

Biology
The head louse variant attaches eggs (nits) to the base of hair shafts, whereas body lice glue their eggs to projecting fibers of clothing on their host. Find out more about the development of their young.
-
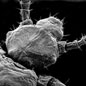
Behaviour
Human head lice are capable of adapting to the different ecological conditions on the human scalp, torso or clothin feeding on blood. Discover more about their behaviour.
-

Significance to humans
Pediculus humanus head louse variant is common in the western world, with infection the principal vector of epidemic typhus (Rickettsia prowazekii), the body louse variant is responsible for hundreds of millions of deaths up until the early nineteen hundreds.Find out more.
About the author
Dr Vince Smith
Cybertaxonomist, Entomology Systematics and Evolution, Department of Entomology.
