Biology
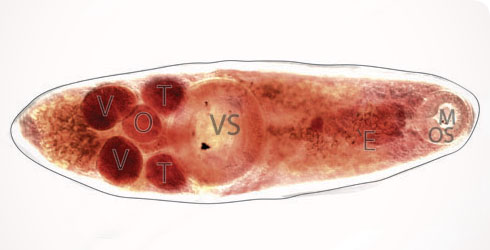
The body - or soma - of Derogenes varicus has two suckers and an inverted U-shaped intestine.
Lifecycle
Derogenes varicus typically has a three host life-cycle and lives in
- a marine snail
- another invertebrate, then
- a fish, in which the adult develops
In some cases other hosts may be fitted into the cycle.
In the stomach of the fish, the worms develop into fully mature hermaphroditic adults, with testes and ovary, and continuously produce a flow of eggs which are shed into the fish gut and pass out in the host’s faeces.
These eggs are consumed by the snail where they hatch into a motile larva - miracidium.
The miracidium moves to the digestive glands of the snail and transforms into a sac-like stage called the mother sporocyst.
The mother sporocyst produces - by asexual reproduction - another generation called rediae. These are similar to the sporocyst, but have a gut and pharynx.
Each redia gives rise to many cercariae - motile larvae with a tail - which emerge from the redia and then the snail.