Taxonomy
- Sac-like stages consist of an outer and inner epithelial tissue layer.
- Cell doublets and pseudoplasmodial stages develop in fish kidney.
- Spores consist of valve cells that form the spore wall, capsulogenic cells that produce polar capsules, and infective sporoplasm cells.
- Polar capsules are intracellular organelles in spores of all myxozoans and which share a common ancestry with nematocysts found in the stinging cells of cnidarians.
Diagnostic description
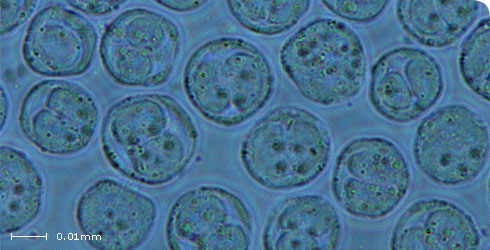
Sacs are uniformly round and up to 0.35 mm in diameter.
This species is commonly found in the bryozoan Fredericella sultana although DNA sequence data indicate that other bryozoans can also act as hosts (Anderson et al. 1999). Since these parasites are highly reduced and lack many distinguishing features, DNA sequence analysis is primarily used for species confirmation.
Lookalikes
Other myxozoan parasites that produce sac-like stages in freshwater bryozoans may be confused with Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae. However, Buddenbrockia allmani has only been recorded from the bryozoan Lophopus crystallinus while B. plumatellae is found in the bryozoan Cristatella mucedo.
Furthermore, the sac-like stages in these two species are generally irregular or oval in shape. Those produced by T. bryosalmonae are uniformly round. DNA sequences can also distinguish species (Tops et al. 2005).
Note
This classification is the one that is best supported but the myxozoans have not formally been recognised as cnidarians.