Mandragora caulescens (Himalayan mandrake)
Mandragora caulescens is a perennial herb with bell-shaped dark purplish black flowers and round green berries. It has a sturdy taproot that may become elongated and branched.
It is a member of the mandrake genus which includes two other species, Mandragora officinarum L. and Mandragora turcomanica Mizg.
Mandragora caulescens is found in southwest Asia and has a Sino-Himalayan distribution.
Its roots have been used in herbal medicines for hundreds of years. They contain several active ingredients with hallucinogenic properties.
Species detail
The roots of Mandragora caulescens contain the tropane alkaloids hyoscine and anisodamine, which are used in local medicine. Anisodamine is used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China.
-

Taxonomy
Discover what distinguishes the Himalayan mandrake from its Mediterranean relatives.
-

Distribution
Mandragora caulescens is native to China and other parts of Asia. It thrives in open moorland and on grassy slopes. Find out more.
Images

Illustration of Mandragora caulescens from Flora of China Illustrations, volume 17, CB Clarke.

Roots of the Mandragora caulescens.

Herbarium specimen of Mandragora caulescens.

Herbarium specimen of Mandragora caulescens.
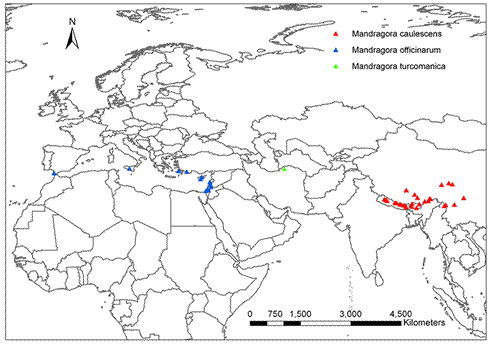
Distribution of herbarium records of Mandragora species.
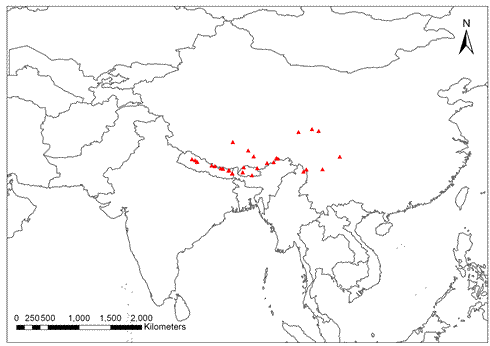
Distribution of herbarium records of Mandragora caulescens.
About the author
Guy Atchison
Former Chinese plants data entry and content development assistant
Department of Botony
