Lifecycle
Like all true parasites, Anthosoma crassum is dependent upon its fish host for completion of its lifecycle.
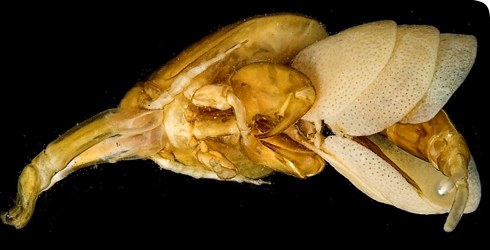
- Females produce a pair of long cylindrical egg strings
- each containing a single stack of flattened, disc-like eggs.
- Eggs hatch as nauplius larvae which are
- non-feeding
- nourished by the yolk they contain
- generally only 2 nauplius stages in these copepods
- the second nauplius larva stage moults into the infective stage – the copepodid.
- the copepodid locates a host
- not known how
- in related copepods parasitic on fish, host location involves
- behaviour that initially brings the larva into the correct habitat to encounter a host, where
- larva responds to the presence of a host detected by
- sensing the mechanical disturbance caused by the host’s swimming
- or visually as a shadow passing overhead.
- The final stage of infection , recognising the correct host
- usually depends upon detecting chemicals contained in the fish mucus or skin.