Taxonomy
Morphology
Ixodes ricinus is a tick (order Ixodida) because it has:
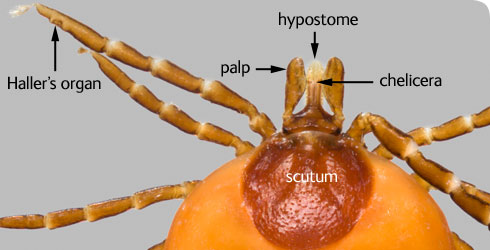
- backwardly-pointing teeth on the hypostome
- a Haller’s organ on the terminal segment (tarsus) of the front legs -each organ comprises a pit and capsule containing hair-like sensory structures (setae)
- the external respiratory openings (spiracles) are located on a pair of spiracular plates
It is a hard tick (family Ixodidae) because:
- the gnathosoma (the mouthparts) – comprising the hypostome, palps and chelicerae - is large and clearly visible from above in all life stages
- the upper body surface is partly (larva, nymph, female) or completely (male) covered by a hardened shield (scutum)
The anal groove arching in front of the anus is only seen in the genus Ixodes.
Adult specific character states are:
- the female scutum is almost circular
- the basal segment (coxa) of the first pair of legs (legs I) has a long, slender internal spur
- all leg coxae have a small external spur
- the tarsi of legs I taper towards their apex
- the female genital aperture is between leg coxae IV
Look-alikes
Ixodes hexagonus Leach – the hedgehog tick - has a similar distribution to I.ricinus and parasitizes many of the same host species.
It can be easily identified by the hump near the apex of tarsus I (absent in I.ricinus), the female genital aperture being between coxae III and not IV, and the rounded hexagonal, rather than circular, scutum.