Fredericella sultana
Fredericella sultana is one of the most common freshwater bryozoan usually found in flowing or turbulent rivers and streams however it also inhabits ponds, lakes and canals.
Fredericella sultana is the most common host of the myxozoan parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae. Infective stages of T. bryosalmonae are released from Fredericella sultana causing Proliferative Kidney Disease (PDK). PDK is an economically devastating disease of wild and farmed salmonid fish (Anderson et al., 1999; Feist et al., 2001).
Species detail

Fredericella sultana lophophore is circular
Like all freshwater bryozoans, Fredericella sultana forms colonies.
Fredericella sultana colonies
- are composed of identical zooids.
- each zooid has a crown of feeding tentacles, the lophophore
- have a tough chitinous outer wall
- attach to natural and man-made submerged surfaces (Wood and Okamura, 2005).
- can resemble plants, as suggested by the common name for bryozoans, the ‘moss animals’
-

Taxonomy
Read about the form and structure of Fredericella sultana, find out its distinguishing features and learn about similar looking species.
-

Distribution and ecology
Discover the areas of the world that Fredericella sultana is known from and the types of habitat it is found in. Learn about the feeding patterns of this species.
-

Biology
Fredericella sultana forms colonies composed of identical zooids. Find out about the size and growth patterns of these colonies and zooids and learn about the lifecycle and life expectancy of this species.
-

Reproduction and dispersal
Asexual production is the main reproductive mode while sexual reproduction is rare. Find out more about the reproductive patterns of this species. Learn how Fredericella sultana achieves dispersal
-

Behaviour
Learn about the interactions that Fredericella sultana has with other species and the diseases it can harbour.
-

References
Get reference material for Fredericella sultana.
Images

Fredericella sultana, a branching freshwater bryozoan.
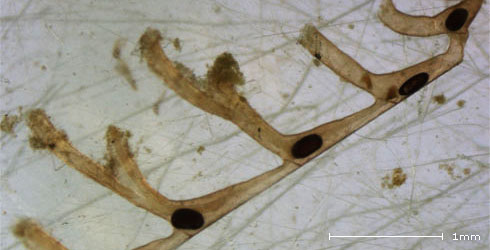
Dark brown statoblasts retained inside branches.

Tree roots are a common habitat of F. sultana.
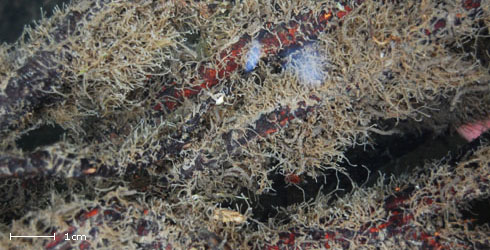
Dense clumps of F. sultana growing on submerged tree roots.
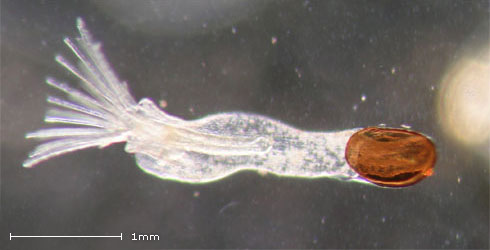
Hatching statoblast F. sultana.

F. sultana lophophore is circular.
Author
Hanna Hartikainen
Bryozoa Research Assistant, Department of Zoology.
Toolbox
Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae - 22/03/2010
Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae is a multicellular endoparasite known for causing proliferative kidney disease in trout and salmon, which has resulted in significant economic losses for aquaculture and has threatened wild fish populations. Find out more about Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae.
