Flustra foliacea (broad-leaved hornwrack)
Flustra foliacea (Linnaeus, 1758) is a cheilostome marine bryozoan that is commonly found along the strand line, or high-tide mark, around the British coast especially after storms.
It has a distinctive lemon-like smell when fresh.
Known as the broad-leaved hornwrack, this bryozoan forms bushy flexible colonies 6–20cm in height, that are light grey-brown in colour.
It is often mistaken for a seaweed.
Species detail
-

Taxonomy
Bryozoans consist of individuals called zooids that form a colony. Find out how you can identify Flustra foliacea colonies.
-

Distribution
This bryozoan is found in cold water areas on stony ground and forms a rich microhabitat for other animals. Find out more.
-

Biology
Flustra can grow for at least 12 years and forms annual growth lines, similar to rings in a tree.
-

References
Get reference material for Flustra foliacea.
Images
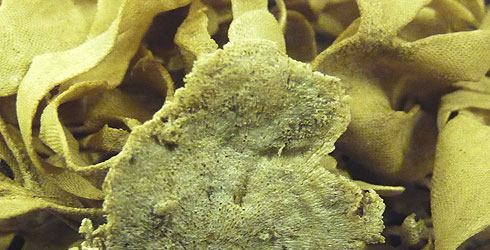
Base of Flustra where it adheres to substrate.
© Natural History Museum, London
Flustra foliacea fronds.
© Natural History Museum, London
Electra pilosa encrusting Flustra foliacea.
© Natural History Museum, London
Flustra foliacea habitat.
© Dorset Seasearch
Original description of Flustra foliacea from Linnaeus, 1758.
© Natural History Museum, London
R Hooke's Micrographia.
© Natural History Museum, London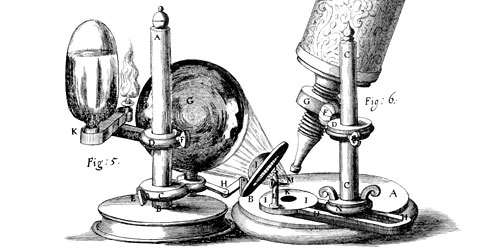
R Hooke's microscope.
© Natural History Museum, London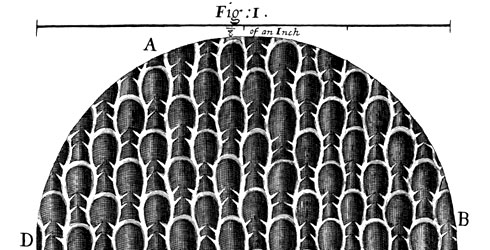
Structure of Flustra foliacea.
© Natural History Museum, LondonAbout the author

Miss Mary Spencer Jones
Senior Curator (Bryozoa) on the Invertebrates Curation Team. Research focuses on the history and biodiversity of marine bryozoans and the preservation, maintenance and conservation of invertebrate collections.

